(7 min. read)

Table of Contents
When it comes to multi-language sites, there are some concerns about how to properly set them up. There are three popular ways to create different language variants of one domain:
- A folder in the main domain: http://
example.com/ de - Subdomain: http://
de.example.com - Top-Level Domain (TLD): http://
example.de
Which solution is best?
From an SEO perspective, there is no one sure solution to this problem. Various language versions in subfolders inherit the ‘Strength” of the main domain. Different Top Level Domains for each language version, on the other hand, need different external links leading to them, while a part of the value of the links directing to one domain with language subfolders is divided between all of the pages, including other language versions.
Subfolders are a good way to lower the cost of SEO for the multi-language page. In addition to the shared strength of the domain and external links, there are two other beneficial factors. The first one: Links from other TLDs of the same type are more valuable for your TLD. For example, if you have a different language version on a top level domain – http://
There is one disadvantage of a subfolder in Top Level Domain – it is much harder to achieve top positions in search results in other countries with your native domain, for example – you won't rank as high with an English Top Level Domain with subfolder co.uk/
Using a subdomain can be considered a compromise between the folder and separate TLD. Its SEO effectiveness is a bit restricted because subdomains are not treated by Google as good as top levels. But, if you have a valuable domain name which has garnered a lot of reputation over the years and has a significant “Strength”, it will leak its value to its subdomains which will immensely help in Search Engine Optimisation.
Of course, when you try to decide which option is the best for you, you should not only think about SEO, but also about other factors, such as:
- type of the service (shop, blog, classifieds, business page)
- technical aspects (CMS, framework, shopping platform)
- Aims of your site
- Business and marketing strategy
- Number of language variants
As you can see, making this decision is not easy, as you have to analyse your business model and devise a plan. In addition, you should also think about user experience.
Hreflang – how to be liked by Google
Choosing the method of publishing the language version on the web is only the first step in a complicated SEO process. You should also properly tag language properties of each and every language version to make it clear for Google bots to interpret and display the data. Google recommends a “Hreflang” attribute. It informs the bots which pages relate to a certain language and location. Additionally, hreflang can be used for subdomains, TLDs, and folders.
There is one more thing – hrelfang helps you avoid duplicate content. If you have two variants of the page in very similar languages (for example – different English versions for USA, UK, Ireland and Australia) standard indexing would make them all duplicates. If you properly configure the hreflang attribute, Google treats each of them as a regional counterpart instead of duplicate content.
When it comes to technical aspects, implementation of hreflang is not too difficult. You can utilise one of three methods:
1. HTML in the <head> section
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="pl" href="http://
2. HTTP Header, like
Link: <http://
This solution is useful for publishing content which is not in the HTML format (like PDF).
3. XML Sitemap, i.e.
<url>
<loc>http://
<xhtml:link
rel="alternate" hreflang="es" href=http://
<xhtml:link
rel="alternate" hreflang="pl" href=http://
</url>
The solution above can be used for different versions in the folders of the same domain.
The easiest way to see if the hreflang attribute was implemented correctly is by using Google Search Console. In the “Traffic” section you can find the “International Targeting” tab. You can see the data regarding the hreflang attribute and errors found by bots.
URLs shown here can display two types of errors:
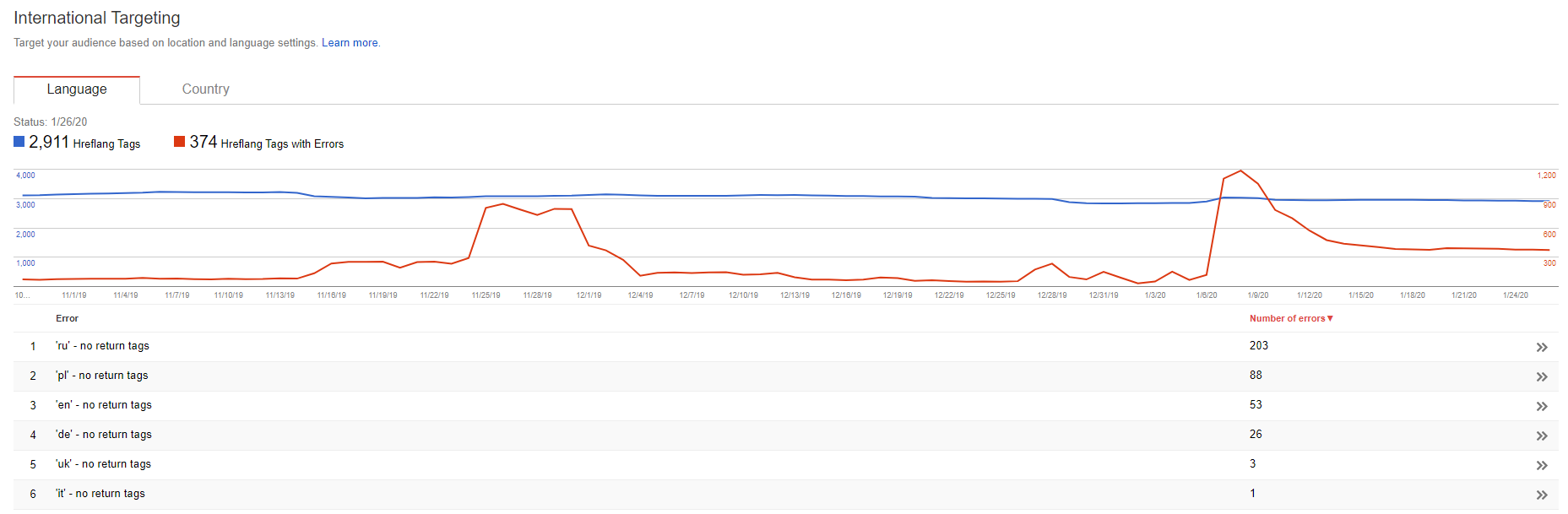
- No return tag
If page A directs to the alternative Site B, Site B has to direct to Site A
- Unknown language code
The language in hraflang value should be set in ISO format (for example "ISO-639-1") and the optional region has to be set as in the following example: "ISO-3166-1 alfa 2". Let's take these examples:
- de - German content, regardless of the region
- en-GB - English version for United Kingdom location
- de-ES - German version for users in Spain
You should also remember that if the address has different language versions, they should direct to other variants, not to themselves. For example - if a Polish site has German and Italian variants, Italian one has to direct to the German and Polish versions and so on.
Moreover, if the domain has a Home Page with a language selection option or automatically redirects to the appropriate variant using user's location, you should set the attribute value of "x-default", i.e. <link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="http://
It is also crucial to use hreflang to signify alternate URLS not only for the same domain but also for the subdomains and TLDs.
What else should be noted?
Aside from implementation of hreflang, there are other practices which are recommended for multi-language, global sites:
- Each language version should include visible language selection that leads to other variants. It is not only user-friendly but helps Google bots index different versions.
- Even if you use hreflang, you should also place the language information in the <head> section of the domain, i.e:
<meta http-equiv="content-language" content="en" /
or using a tag
<html lang="en-GB">
This way you make it easier for bots to classify your language versions correctly.
When you have alternate variants on the same domain, you have to remember not to set one global language for all subpages but to do it separately for each version/
- You can also configure your default location using Google Search Console “International Targeting” option.
Different settings regarding the location can be chosen for each subdomain, TLDs or subfolders of the same domain (but you have to add all variants to Google search console first).
Summary
Preparing the same content in different languages is not an easy and cheap task. You have to carefully choose the best option for publishing the variants of your site in accordance with the line of business you deal with. To make sure all this work does not go to waste, you should follow Google guidelines. This way you can be certain the process of indexing will be smooth and clear, and the relations between different language/
Author: Maciej Dobkowicz, SEO Account Manager at SEMTEC



